Introduction
OpenDT is a Shadow Mode Digital Twin for datacenters. It connects to a real datacenter (or a mock of one) and replays workload data through the OpenDC simulator, comparing predicted power consumption against actual measurements in real time.
Key Capabilities
- Power Prediction: Estimate power consumption based on workload patterns
- What-If Analysis: Test infrastructure changes without touching live hardware
- Active Calibration: Automatically tune simulation parameters to minimize prediction error
- Carbon Estimation: Calculate carbon emissions from power draw and grid intensity
Architecture Overview
OpenDT bridges physical and digital infrastructure through a modular design:
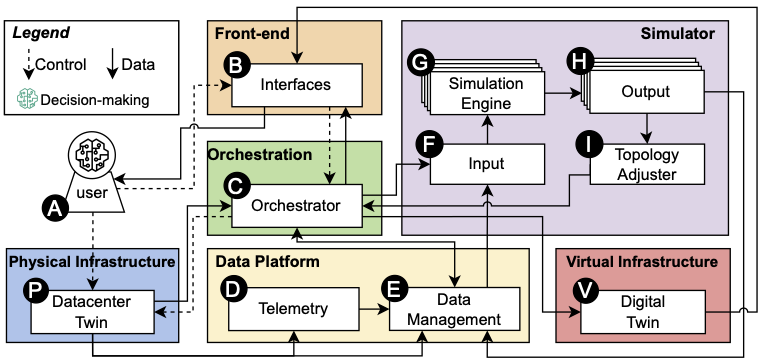
| Component | Purpose | OpenDT Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Infrastructure (P) | Data source | dc-mock service |
| Front-end (B) | User interfaces | Grafana + REST API |
| Orchestration (C) | Message routing | Kafka |
| Data Platform (D, E) | Telemetry & storage | Parquet files |
| Simulator (F-I) | Power prediction | OpenDC + calibrator |
| Virtual Infrastructure (V) | Digital twin state | Topology configuration |
See the Architecture page for detailed component mapping.
Data Flow
- dc-mock reads historical workload and power data from Parquet files
- Messages are published to Kafka topics with configurable speed factor
- simulator consumes workload messages, aggregates them into time windows, and invokes OpenDC
- api queries results and serves them to the Grafana dashboard
Use Cases
Reproduce Experiments
Run predefined experiments with the Reproducibility Capsule:
make up config=config/experiments/experiment_1.yaml
Explore What-If Scenarios
Modify the datacenter topology and observe how power consumption changes:
- Upgrade CPU architecture
- Change power model parameters
- Add or remove hosts
Validate Power Models
Compare different power model types (MSE, Asymptotic, Linear) against real measurements to find the best fit for your hardware.
Quick Start
See the Getting Started guide to run your first simulation.